AHCC®
Shiitake alpha-glucans for immune support
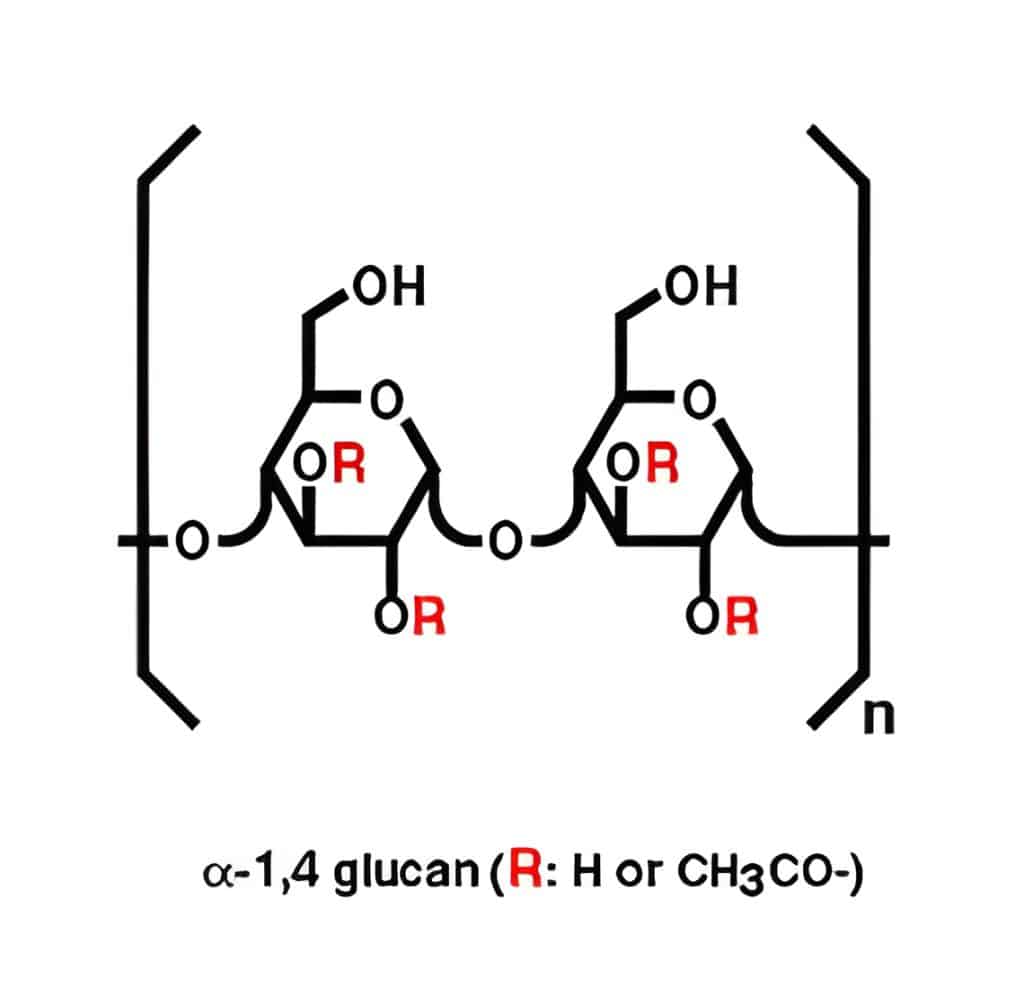
AHCC® : unique active compounds generated by a proprietary production process
AHCC® is produced by a patented process developed in the 1980’s by the Japanese company Amino Up Co., in collaboration with the University of Tokyo. Shiitake cells grown in a proprietary liquid culture system produce and release in the medium some specific active components called acylated alpha-glucans. Alpha-glucans are small molecules easily absorbed by the organism, which exert a number of beneficial effects including modulation of the gut microbiota and stimulation of the immune system. The properties of AHCC® have been described in more than 100 scientific articles (more than 75 referenced on Pubmed), including reports of more than 30 human clinical studies. AHCC® is Japan’s top-selling immune support ingredient and is now used in more than 40 countries all over the world. It has been used in Europe for more than 30 years.
AHCC® and immune function
A large number of scientific and clinical studies have investigated the effects of AHCC on immune cells, especially NK cells and cytotoxic T-cells. AHCC® has been shown to stimulate the immune function in healthy subjects, at the beginning of the cold season. AHCC® exerts positive effects on both innate and acquired immunity. Its overall stimulating effects on immunity make it suitable for use in many different clinical settings.

AHCC® and intestinal health
70 to 80% of all our immune cells are located in the gut. Compounds in the gut lumen can interact with immune cells and modulate systemic immune function. Research has shown that AHCC® components interact with specific receptors at the surface of epithelial and immune cells, called Toll-Like Receptors. Besides, AHCC® has a prebiotic effect and modulates positively the composition of the gut microbiota, increasing lactic acid bacteria, such as Bifidobacteria, and reducing the populations of potentially pathogenic Clostridia.
Liver function and detoxification
Human clinical trials have shown that AHCC® can protect the liver against various types of damages : it improves the markers of liver damage in alcoholic fatty liver patients, and also had a protective effect in the context of hepatitis C infection. AHCC® protects liver cells against oxidative damage, inhibits the expression of pro-inflammatory gene iNOS. By supporting liver function, AHCC® allows a better elimination of toxins.
Safety of AHCC®
AHCC® has been used in clinical practice for more than 35 years. In vitro and animal toxicity studies, as well as a human phase I clinical study, have proven AHCC® to be safe and devoid of side effects.

Selected references
- Aviles et al. 2008. Active hexose correlated compound activates immune function to decrease bacterial load in a murine model of intramuscular infection. Am J Surg. vol. 195(4).
- Ito et al. 2014. Reduction of adverse effects by a mushroom product, active hexose correlated compound (AHCC) in patients with advanced cancer during chemotherapy – The significance of the levels of HHV-6 DNA in saliva as a surrogate biomarker during chemotherapy. Nut Cancer vol. 66(3).
- Kim et al. 2014. Effect of active hexose correlated compound (AHCC) in alcohol-induced liver enzyme elevation. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol. vol. 60(5).
- Matsui et al. 2011. Active hexose correlated compound inhibits the expression of proinflammatory biomarker iNOS in hepatocytes. Eur Surg Res. vol. 47(4).
- Nogusa et al. 2009. Low dose supplementation with active hexose correlated compound improves the immune response to acute influenza infection in C57BL/6 mice. Nutr Res. vol. 29(2).
- Roman et al. 2013. Short-term supplementation with active hexose correlated compound improves the antibody response to influenza B vaccine. Nutr Res. vol. 33(1).
- Takanari et al. 2015. Effects of active hexose correlated compound on the seasonal variations of immune competence in healthy subjects. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. vol. 20(1).
- Terakawa et al. 2008. Immunological effect of active hexose correlated compound (AHCC) in healthy volunteers: a double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr Cancer vol. 60(5).
- Yin et al. 2010. Effects of active hexose correlated compound on frequency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells producing interferon-gamma and/or tumor necrosis factor-alpha in healthy adults. Hum Immunol. vol. 71(12).
- Graham et al. 2017. MicroRNA signature in the chemoprevention of functionally enriched stem and progenitor pools (FESPP) by Active Hexose Correlated Compound (AHCC). Cancer Biol Ther. vol. 18(10).
- Smith et al. 2019. From bench to bedside: evaluation of AHCC supplementation to modulate the host immunity to clear high-risk human papillomavirus infections. Front Oncol. vol. 4(173).
- Smith et al. 2022. AHCC® supplementation to support immune function to clear persistent Human Papillomavirus Infections. Front Oncol. doi 10.3389/fonc.2022.881902.
- Park et al. 2022. AHCC®, a standardized extract of cultured Lentinula edodes, promotes the anti-tumor effect of Dual Immune Checkpoint Blockade effect in murine colon cancer. Front Immunol. doi 10.3389/fimmu.2022.875872.

